Start practice on hydrocarbon
1. Alkane
1. Which give CH4 when treated with water
- Aluminium carbide
- Calcium carbide
- Silicon carbide
- Iron carbide
ans : a
2. A reaction between methyl magnesium bromide and ethyl alcohol gives
- Butane
- Ethane
- Propane
- Methane
ans : d
ans : a
ans : c
5. Iodoethane react with sodium in the presence of dry ether the product is
- Pentane
- Butane
- Butene
- Propane
ans : b
6. Which of the following has maximum boiling point ?
- n-octane
- iso-octane
- 2,2,3,3-tetramethyl butane
- n-butane
ans : a
ans : b
8. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of heat evolved when one mole of each of them is hydrogenated using Pt-catalyst.
- I < II < III < IV
- III < I < II < IV
- IV < II < III < I
- IV < I < II III
ans : d
9. Which of the following cannot be formed as single major product by wurtz's coupling reaction of an alkyl halide ?
ans : b
10. The compound given below is chiral. What would be the outcome of catalytic hydrogenation of a pure enantiomer of this compound
- A pair of enantiomers in euqal would be produced
- A pair of diastereomers in unequal amount would be produced
- both (a) and (b)
- none of these
ans : b
11. C6H12 (x) has only two types of alkenes that can be reduced to only one type of alkane C6H14 (y) . y is ?
ans : b
12. To prepare a pure sample of n- hexane using sodium metal as one reactant, the other reactant will be.
- Ethyl chloride and n-butyl chloride
- Ethyl bromide and n-butyl bromide
- n-propyl bromide
- None of these
ans : c
13. Which of the following is oxidized by KMnO4
- Methane
- Isobutane
- Pentane
- Neopentane
ans : b
14. Which of the following is not an endothermic reaction ?
- Combustion of propane
- Ethane to ethene
- Dehydrogenation
- Change of chlorine molucule into chlorine atoms.
ans : a
15. Photochemical chlorination of alkane is initiated by a process of
- RCHO
- CO2
- RCOOH
- RCOOOH
ans : b
16. Aromatization of n-heptane by passing over (Al2O3+Cr2O3) catalyst at 773 k gives
- Benzene
- Mixture of both
- Toluene
- none of these
ans : c
17. Normal butane is converted into isobutane by
- LiAlH4
- Zn/Hcl
- NaBH4
- AlCl3
ans : d
ans : b
19. How many dichlorocyclohexane would be produced upon free radical chlorination of chlorocyclohexane ?
- 4
- 6
- 9
- 8
ans : c
- 1
- 2
- 4
- 3
ans : c
2. Alkene
1. How many different alkenes are formed when 2-chlorobutane is treated with ethanoic solution of KOH ?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
ans : c
2. Sodium ethoxide is a specific reagent for
- Dehydration
- Dehydrogenation
- Dehalogenation
- Dehydrohalogenation
ans : d
3. Ethyl bromid gives ethylene when reacted with
- Ethyl alcohol
- Alcoholic KOH
- Aqueous KOH
- Dilute H2SO4
ans : b
- Propyne
- Propanol
- Propene
- Propane
ans : c
5. During debromination of meso-dibromobutane, the major compound formed is
- n-butane
- 1-butane
- trans-2-butene
- cis-2-butene
ans : c
- Sulphonation
- Alkylation
- Dehydration
- Decomposition
ans : c
7. 1,2-dibromoethane when heated with alcoholic potash gives
- Ethane
- Ethylene
- Acetylene
- Methane
ans : c
8. When two alkenes may be formed by dehydrohalogenation of an alkyl halide, the alkene which is more substituted is the major or preferred product. This generalisation is Known as
- Markownikoff's rule
- Anti-Markownikoff's rule
- Saytzeff rule
- None of these
ans : c
ans : d
10. find wrong option for stability
- 2,3-Dimethylbut-2-ene > 2-Methylpent-2-ene
- trans-Hex-3-ene > cis-Hex-3-ene
- Cis-Hex-3-ene > Hex-1-ene
- trans-Hex-2-ene > 2-Methylpent-2-ene
ans : d
ans : a
12. Which one of the following compounds does not form an ozonide ?
- Propane
- Propyne
- Propene
- Ethene
ans : a
ans : d
14. Which reactions are most common in alkenes ?
- Electrophilic addition reactions
- Nucleophilic substitution reactions
- Electrophilic substitution reactions
- Nucleophilic addition reactions
ans : a
15. Which one of the following characteristics apply to both ethene and ethyne
- Explode when mixed with chlorine
- From white precipiate with silver nitrate solution
- Rapidly absorbed by cold conc H2SO4
- Declorize Baeyer's reagent giving brown precipitate
ans : d
ans : a
17. Ozonolysis of 2-methyl butane-2 yields
- Both aldehyde and ketone
- Only ketone
- Only aldehyde
- None of these
ans : a
18. Propylene on hydrolysis with sulphuric acid forms
- n-propyl alcohol
- Ethyl alcohol
- Isopropyl alcohol
- Butyl alcohol
ans : c
19. An alkene , on ozonolysis, gives formaldehyde and acetaldehyde. the alkene is :
- Ethene
- Butene
- Butene-1
- Propene
ans : d
20. Position of double bond in an organic compound is determined by
- Oxidation
- Ozonolysis
- Reduction
- Hydrogenation
ans : b
21. Addition of HI on the double bond of propene yields isopropyl iodide and not n-propyl iodide as the major product. This is because the addition proceeds through
- A more stable free radical
- A more stable carbanion
- A more stable carbonium ion
- None of these
ans : c
22. The only alcohol that can be prepared by the indirect hydration of alkene is
- Isobutyl alcohol
- Propyl alcohol
- Ethyl alcohol
- Methyl alcohol
ans : c
3. Alkyne
1. How many isomers exist with the formula C4H6 ?
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 9
ans : d
2. The shortest -C-H bond is present among the following in
- C2H6
- C2H4
- C2H2
- Same length
ans : c
3. Which of the folllowing molecule is totally linear
- ethane
- Ethylene
- Benzene
- Acetylene
ans : d
4. When chloroform is heated with Ag. the compound formed is
- Ethane
- Methane
- Ethylene
- Acetylene
ans : d
5. The reagents required to convert acetylene into ethylene is
- Na, NH3
- H2, Pd, BaSO4 quinoline
- H2/Ni
- Na , C2H5OH
ans : b
6. The reagent which convert but-1-yne into but-2-yne is
- Na , NH3Cl
- NaNH2 , NH3
- alcoholic KOH
- NaOH
ans : c
7. The reagent which convert but-2-yne into but-1-yne is
- Alc KOH
- NaOH
- NaNH2
- a or c
ans : c
ans : a
9. The correct increasing order of heat evolved when 1.0 mole of each of the following is hydrogenated completely is
- II < I < IV < III
- III < IV < I < II
- I < II < IV < III
- None of these
ans : a
ans : d
ans : c
12. But-2-yne is treated with Na, liquid Nh3 , The product is
- Butane
- Cis but-2-ene
- Trans but-2-ene
- A mixture of both cis and trans but-2-enes
ans : c
ans : b
ans : b
ans : c
16. In which of the following ,the bond length between carbon and carbon atom is equal
- 2-butene
- 1-butene
- Benzene
- 1-propyne
ans : c
17. When propyne reacts with aqueous H2SO4 in the presence of HgSO4, the major product is
- Propanal
- Acetone
- Propyl hydrogen sulphate
- None of these
ans : b








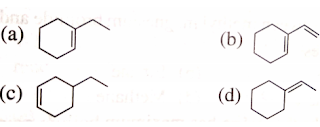



















Comments
Post a Comment